A 3-way valve is a vital component across numerous fluid control applications, including HVAC, industrial process systems, engine cooling circuits, and domestic hot water regulation. This technical guide outlines its purpose, operational mechanics, fault indicators, diagnostic protocols, and frequently asked questions.

Find new 3 way valve online
✅ Purpose of a 3-Way Valve
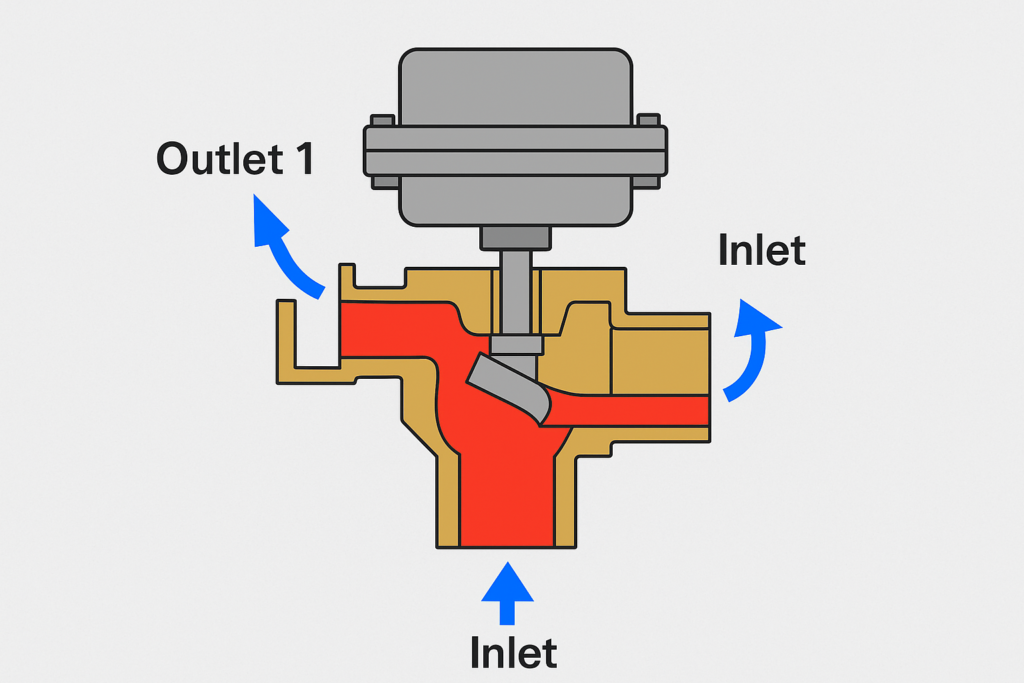
A 3-way valve is engineered to manage fluid direction and flow via three distinct ports. It provides advanced control capabilities by allowing either:
- Diverting Mode: Redirecting a single fluid stream to one of two separate outlets.
- Mixing Mode: Combining two incoming fluid streams into a single outlet.
- Zone Control: Distributing fluid based on zone-specific requirements, improving energy efficiency.
These functionalities support precise thermal regulation, optimal resource usage, and enhanced comfort or industrial output.
⚙️ Working Principle of a 3-Way Valve
- Common Port (C): The central port; entry or exit depends on application.
- Port A & Port B: Auxiliary flow channels for input or output.
Modes of Operation:
- Diverting: Fluid enters through the Common Port and exits through either Port A or B. Only one outlet is open at a time.
- Mixing: Fluids enter via Ports A and B and exit through the Common Port. Internal mechanics regulate blend ratios.
Actuation Types:
- Manual: Hand-operated levers.
- Thermostatic: Wax or bimetallic actuators for temperature response.
- Electric (Motorized): Integrated with BMS or thermostats.
- Pneumatic: Diaphragm or piston actuation using air pressure.
- Solenoid: Electromagnetic switching for fast response.

Find new 3 way valve online
⚠️ Common Symptoms of a Faulty 3-Way Valve
- Inconsistent outlet temperature
- No flow or low flow in designated outlets
- Unusual pipe noises (e.g., water hammer)
- Leaks at housing or actuator stem
- Non-responsive or erratic actuator
- Higher-than-expected energy bills
- Inconsistent performance across heating/cooling zones
💪 Diagnostic Steps for Fault Isolation
- Visual Inspection:
- Check for corrosion, visible leaks, or damage to housing/actuator.
- Manual Override Test:
- Use manual controls to test valve motion and system response.
- Electrical Checks:
- Verify voltage at actuator terminals and test signal continuity.
- Temperature Monitoring:
- Use IR thermometers on inlet/outlet lines to assess blending/diversion accuracy.
- Pressure/Flow Rate Measurement:
- Identify abnormal pressure drops or inconsistent flow paths.
- System Simulation Test:
- Activate thermostat or control logic and observe real-time flow performance.
- Temporary Bypass (Expert-Level):
- Isolate or bypass valve to confirm root cause. Only certified professionals should perform this.

Find new 3 way valve online
❓ FAQs
1. How is a 3-way valve different from a 2-way valve?
- A 2-way valve is linear (one inlet, one outlet). A 3-way valve enables flow direction control (diverting or mixing).
2. Where are 3-way valves typically used?
- HVAC zoning
- Radiant heating
- Domestic hot water tempering
- Engine cooling loops
- Process industries (chemical/gas)
3. Can a 3-way valve be installed in any orientation?
- No. Follow flow direction arrows and actuator mounting guidelines to avoid failure or inefficiency.
4. How do I determine if the valve is mixing or diverting?
- Inspect port connections: 2 inlets + 1 outlet = mixing; 1 inlet + 2 outlets = diverting. Review manufacturer specs.
5. Is maintenance required?
- Yes. Regular cleaning, seal checks, actuator testing, and water quality control are essential.
6. What is the typical lifespan?
- 5 to 20+ years depending on material, fluid type, environment, cycling frequency, and maintenance schedule.
🛠️ Repair Considerations
- Minor Issues:
- Wiring faults, loose actuators, debris accumulation can often be corrected.
- Replaceable Components:
- Cartridges, seals, or actuators may be serviced or replaced in industrial-grade models.
- Major Failures:
- Cracked bodies or seized internals typically require full replacement.

Find new 3 way valve online
🔹 Conclusion
A 3-way valve is a cornerstone of intelligent fluid control, crucial for balancing comfort, energy efficiency, and operational precision. Whether maintaining a domestic heating loop or optimizing an industrial process, understanding and monitoring the performance of your 3-way valve ensures system reliability and longevity.
For advanced diagnostics, integration, or repair, always consult a certified technician and refer to manufacturer specifications.
💼 Affiliate Disclosure
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links. If you click and purchase through them, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. This helps support the content and tools I use to deliver expert guidance. Thank you for your support!
👤 About Me
Hi, I’m Sujith — a mechanical engineer turned content creator with a passion for simplifying technical concepts for professionals and DIYers alike. With hands-on experience in HVAC systems, industrial automation, and digital tools, I write in-depth guides that combine field expertise with clear, actionable advice. Whether you’re optimizing your home system or maintaining industrial equipment, I aim to make your decision-making easier and more informed.